What Does a Compressor Do to Audio? (Explained)
When producing professional-grade audio, it is essential to understand how a compressor works.
Every sound engineer, producer, and artist should understand the basics of signal compression to use the tool effectively.
So, what does a compressor do to audio?
A compressor is designed to increase the overall volume level of an audio signal while also reducing levels in parts that are too loud.
Doing this helps control the dynamic range or, in other words, the difference between the loudest and quietest parts of a sound.
This article will closely examine what a compressor does to an audio signal, from shapes and curves to sonic characteristics.
Key Takeaways
What Is a Compressor?
A compressor is a type of dynamic processor used in audio production. Compressors come in two forms: software and hardware.
Software compressors, also known as plugins, are digital and used inside audio workstations like Pro Tools and Logic Pro X.
Hardware compressors offer more comprehensive control than their plugin counterparts.
What Does a Compressor Do to Audio?
When you apply compression to a signal, it’ll create several sonic characteristics.
First, it’ll help control the transients—or sharp peaks—in your audio that can be too loud and overpowering.
It’ll also reduce the overall dynamic range of your sound by evening out the loud and quiet sections of your audio.
You can also use it to bring up the volume level of an entire signal, making it easier to hear in a mix.
Finally, compressors can add subtle distortion or color to the sound depending on how they’re adjusted.
By adjusting the settings accordingly, you can create various sonic characteristics.
How Does a Compressor Work?
At its core, the compressor process involves two primary components—an encoder and a decoder.
When it finds a part that goes over a set limit, it signals the “compressor” to lower that part’s level.
The compressor then reduces the volume of these parts while leaving other sections untouched.
This helps even out the dynamic range and creates an overall more balanced and uniform sound.
What Are the Basics of Using Compression Effects in Music Production?
To use a compressor in music production, you must balance controlling dynamics and ensuring a pleasing sound.
Below are the basics of using compression effects in music production.
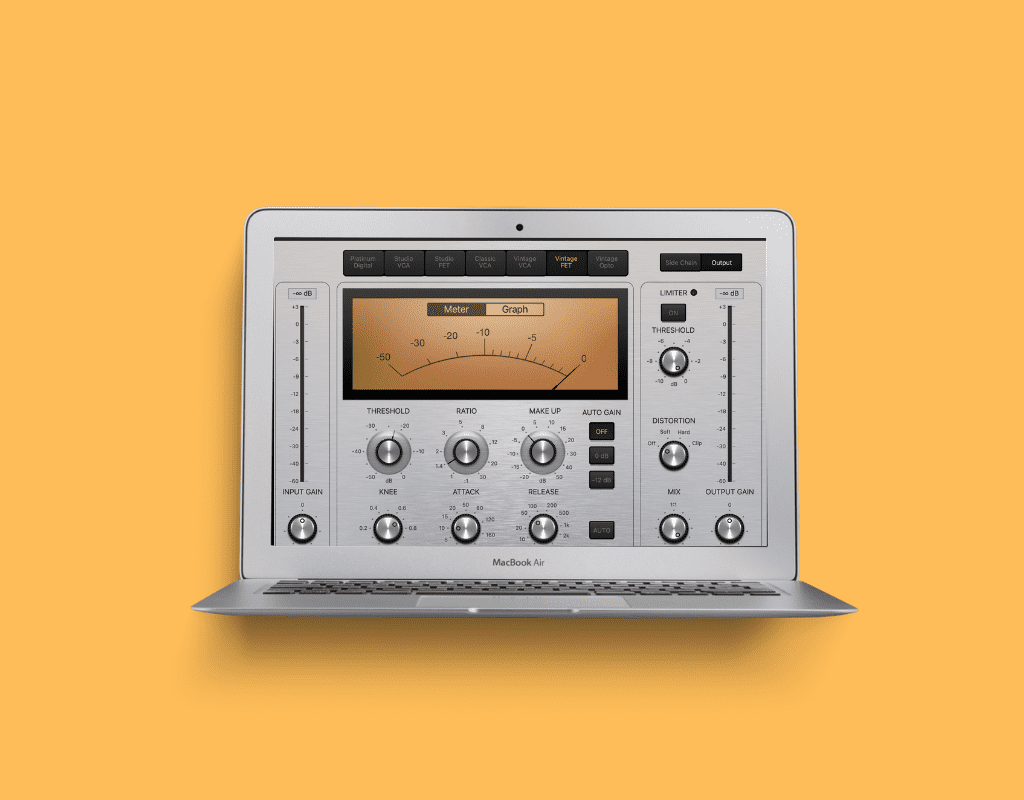
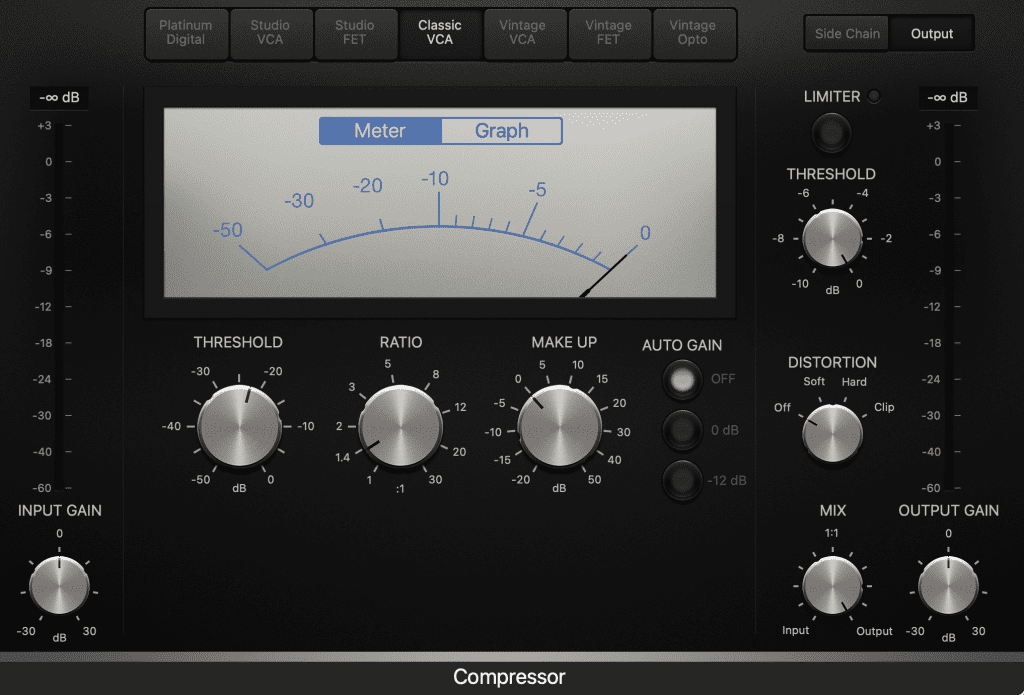
- Set the Threshold: This determines the level at which your compressor will begin to act on the signal.
- Adjust the Ratio: The ratio tells your compressor how much gain reduction it should apply when a signal exceeds the threshold.
- Set an Attack and Release Time: The attack sets how long your compressor will react once a signal exceeds the threshold. Release sets how long it takes for the gain reduction to end.
- Don’t Over-Compress: Too much compression can make the audio sound “squashed” and unnatural. Find the right balance for your sound by starting with small amounts and increasing them as needed.
- Experiment With Different Settings: Compression can achieve a variety of sonic characteristics. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different settings and see what works best for your music.
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to using a compressor.
Every sound will have different settings.
When finding the perfect balance for your audio, it’s important to understand the basics and try different settings.
This will help you fine-tune your sound to your liking.
What Are the Different Types of Compressors?
There are many types of compressors available, each with its unique characteristics.
Some of the most common types include the following:
VCA Compressors

This type of compressor uses a Voltage Controlled Amplifier circuit, which is known for its fast attack and release times.
FET Compressors
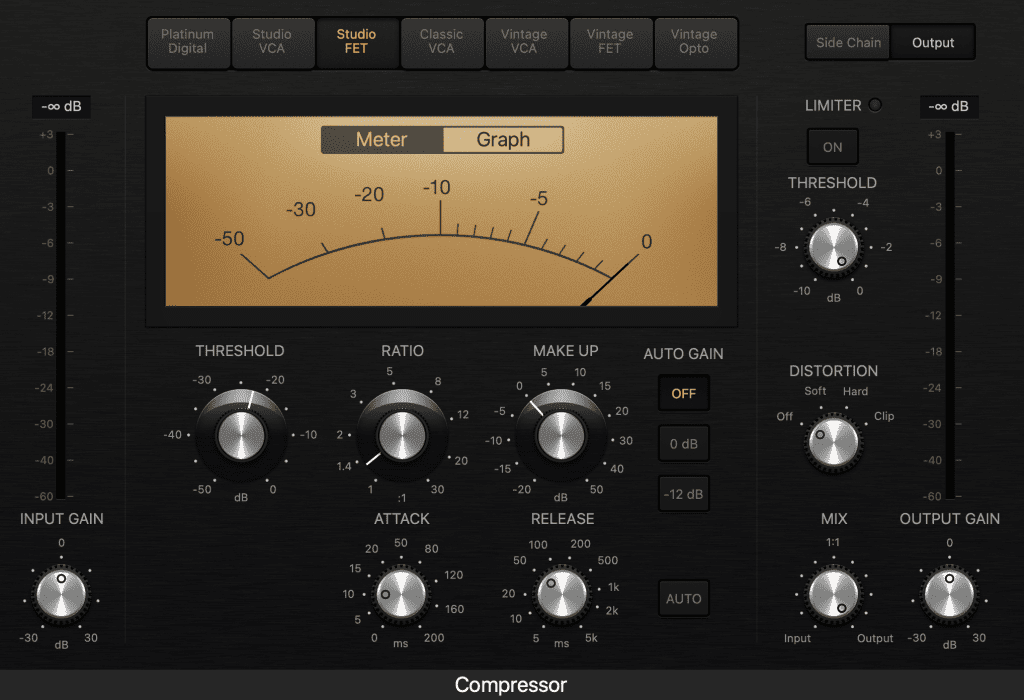
FET (Field Effect Transistor) compressors are highly dynamic and provide a more natural sound.
Optical Compressors
Optical compressors use a visual element to control the amount of gain reduction. They’re known for their smooth, transparent sound.
Multi-Band Compressors
Multi-band compressors allow you to process different frequency bands separately, allowing more precise control over your audio.
By understanding the differences between these various compressors, you’ll be able to choose the best one.
What Are Some Tips to Get the Best Results From Compressors?
- Start with subtle amounts of compression and gradually increase if needed. Too much compression can make a sound unnatural and overly processed.
- Use the attack and Release times to control how your compressor reacts to the signal—experiment with different settings to find what works best for your track.
- Try using multiple compressors in parallel for more control over your audio.
- When mixing, use compression to increase the volume of quieter elements while maintaining the overall dynamic range.
- Try sidechaining a compressor for drums and bass lines to only react when specific instruments are present. This can help create intriguing rhythmic effects.
Final Thoughts
An audio compressor is a tool used in music production that reduces the dynamic range of a track.
This means that the differences between the loudest and quietest parts of the track are brought closer together, resulting in a “louder” overall sound.
There are different types of compressors with various capabilities, so choosing one that will suit your needs is essential.
With some experimentation, you can find the perfect settings to give your tracks the sound you’re looking for.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does audio compression affect sound quality?
Audio compression works by reducing the dynamic range of an audio signal, meaning it decreases the difference between the loudest and quietest parts of the sound. When used appropriately, compression can help maintain a more consistent volume and improve the overall balance of a mix. However, excessive compression may lead to a loss of clarity and audio artifacts, so it’s essential to find the right balance for each specific audio source.
What are the key parameters of an audio compressor?
An audio compressor typically has several key parameters, including threshold, ratio, attack time, release time, and makeup gain (source: iZotope).
The threshold determines the level at which the compressor starts applying gain reduction, while the ratio represents the amount of gain reduction applied once the threshold is exceeded. Attack and release settings control how quickly the compressor reacts to changes in the audio signal, and make-up gain is used to adjust the overall output level after compression.
How to choose the best compressor settings for vocals?
Choosing the best compressor settings for vocals depends on the specific recording and desired outcome. As a starting point, try setting a relatively low threshold (around -20dB to -30dB) and a moderate ratio (around 3:1 or 4:1). Adjust the attack and release times based on the vocal performance’s desired tightness and naturalness, then fine-tune the threshold, ratio, and make-up gain to achieve a smooth, consistent sound.
What are the differences between a compressor and a limiter?
Both compressors and limiters are used to control an audio signal’s dynamic range. However, while a compressor reduces dynamic range by adjusting the gain according to the input level and a specified ratio, a limiter strictly limits the output level, preventing it from exceeding a determined threshold. This results in a higher compression ratio and a more aggressive gain reduction, making limiters more suitable for controlling audio peaks and preventing distortion.
How do expanders differ from compressors in audio?
Expanders are the opposite of compressors in terms of audio processing. While a compressor reduces the dynamic range of an audio signal, an expander works to increase it. Expanders accomplish this by reducing the gain of the audio signal below a specified threshold, making quieter parts even quieter. Expanders can be used to reduce unwanted background noise and enhance the dynamic contrast between quieter and louder sections of an audio source.
What are the benefits of using a compressor in a mix?
Using a compressor in a mix can provide several benefits, such as improved clarity of sounds, better balance between multiple audio sources, and increased loudness without causing distortion. Compression can also help to control transient peaks (e.g., sudden loud noises), making the overall mix smoother and more cohesive. Additionally, compression can be used creatively to shape the tonal characteristics and dynamics of individual tracks within a mix.